
Compare thermal paste and thermal pad | What is best for a laptop
Due to the design features, laptops very often suffer from overheating. All components are located close to each other, and the air inside the case practically does not circulate — and that is why the temperature of the «iron» rises almost exponentially. Overheating, in turn, leads not only to a decrease in performance due to the throttling effect, but also to a reduction in the operating period of the computer and the risk of failure of some parts.
Therefore, it is very important to properly organize the cooling system in the device. And its quality depends not only on the speed of the fans and the cleanliness of the radiators, but also on the thermal conductivity of the «connecting elements» — thermal paste and thermal pads.
In this article, we will figure out what is better for a laptop — thermal paste or thermal pad — and also give some tips on organizing a cooling system.
thermal paste
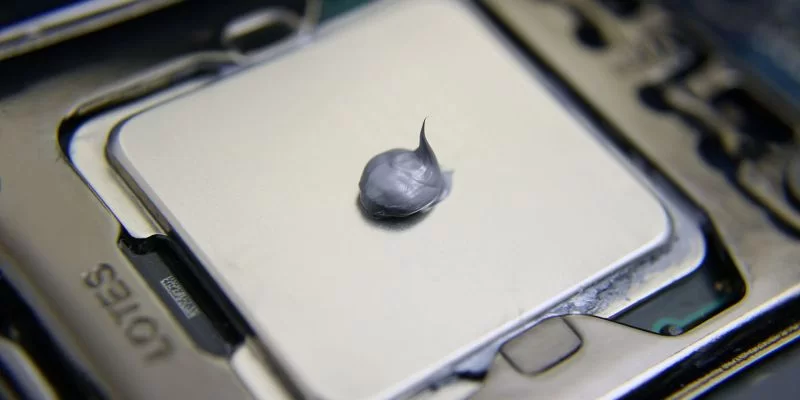

One of the most important conditions for the correct operation of the cooling system is that the heating elements should be located as close as possible to the heat pipes or the contact plate of the radiator. But at the same time, it is required that they contact through a special gasket, which conducts heat.
So, if you attach the contact plate of the radiator to the processor cover, air will remain between these two elements. And he, in turn, is an excellent heat insulator. Air will not pass heat from the processor to the heatsink, and the chip will overheat almost instantly.
Thermal paste is used to prevent this. This emulsion is based on silicone or other liquid material interspersed with metal powder or microcrystals. The liquid component of the thermal paste is needed in order to fill the space between the processor cover. And metal — to conduct heat from the chip to the radiator.
When properly applied, the thickness of the thermal paste layer is close to zero. Its task, as mentioned above, is to push air out of the space between the processor and the heatsink, while ensuring the transfer of high temperature. And, no matter how paradoxical it may be, the more thermal paste is applied, the worse the heat transfer. After all, this is a “grease”, and not butter on a sandwich.
It is very important to note that thermal paste is different. The composition, consistency and — most importantly — thermal conductivity differ. The last one is the most important indicator. The higher the thermal conductivity, the better the thermal paste does its job. So, «grease» with a thermal conductivity above 10 W / mK can reduce the temperature of the processor by 5-10 degrees compared to stock or paste with a value of this indicator less than 5 W / mK.
For laptops, you should take at least 8 W / mK thermal paste. The fact is that the radiators of mobile computers are not very productive in themselves — they are small, unsuccessfully located and easily clogged with dust. Therefore, it is very important that all other elements of the thermal interface are of high quality.
Of course, the price of such a «paste» can be relatively high. Do not expect that it will be cheaper than 10-15 dollars. However, saving on laptop cooling can result in problems with its further work.
So, let’s sum up.
Advantages
-
Perfectly copes with the task of dissipating heat — especially models with a high thermal conductivity value;
-
A wide range — you can find a thermal interface at any desired price and with any desired thermal conductivity.
Flaws
- Relatively high price for really high-quality materials.
In general, thermal paste is a classic solution for cooling equipment. But it is worth remembering that by itself it does not reduce the temperature. This is just a conductor of heat, and specific indicators depend on other elements of the cooling system — a cooler, heat pipes, a radiator, and even a laptop case.
thermal pad
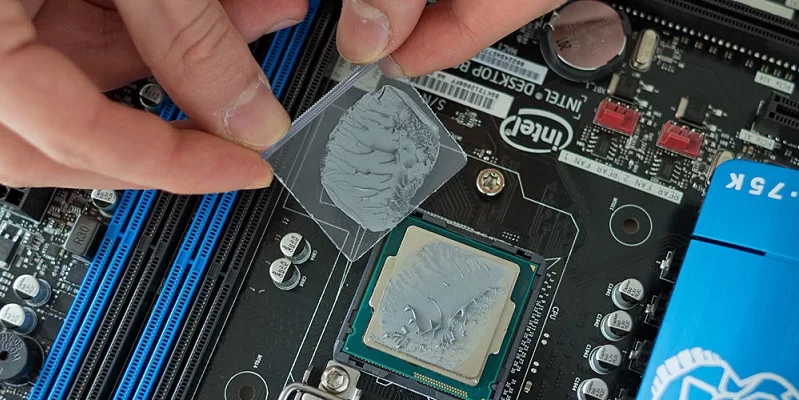
As mentioned above, for effective cooling, the thickness of the thermal paste layer should be minimal. Ideally — 0.1-0.3 mm. But what if the cooled chip itself has a small height, and the contact plate of the heatsink simply does not reach it?
In this case, thermal pads come to the rescue. This is the same thermal interface made of silicone and metal dust, only made in the form of a sheet and having a large thickness (in some cases up to 1-2 mm). It is he who allows you to «connect» the chip and the contact plate of the radiator, acting as a conductor of high temperatures.
Due to their large thickness, thermal pads are less effective than thermal paste, but still more effective than air. As a result, they are used to cool low-performance chips. For example, «weak» discrete video cards or motherboard chipsets. But for processors it is better not to use them. If the manufacturer uses thermal pads to remove heat from the «main chip», this indicates, first of all, the lack of a cooling system and the poor build quality of the laptop itself.
It is worth mentioning that some manufacturers like Gelid or Cooler Master produce thermal pads with high thermal conductivity — from 10 W / mK. However, even they, with their liquid metal and ceramic dust technologies, cannot overcome the laws of physics. These high performance thermal pads are thin, typically 0.5mm thick.
Also, thermal pads have one very important drawback. Cheap models can be made on a thermally unstable silicone or similar base. And under the influence of high temperatures, it can leak, thereby dramatically reducing its effectiveness.
When choosing a thermal pad for a laptop, the same rule applies as for thermal paste: the higher the thermal conductivity, the better. But it is important to consider the location of this thermal interface. For example, in most cases, effective cooling of the chipset is not necessary (except for those situations when a laptop constantly “drives” huge data arrays “back and forth” — for example, a 1C base “spins” on it). So it is not necessary to choose any thermal pads for 10 W / mK — a solution for 5-8 W / mK is enough.
Advantages
-
Ease of placement. It is not necessary to smear the chip with a uniform thin layer, it is enough to cut off a rectangle of the desired size and stick it in place;
-
Variety of models. There are both thin thermal pads and relatively thick ones — from 0.5 to 5 mm.
Flaws
-
High price. Even the least efficient models are comparatively expensive;
-
Relatively low efficiency;
-
There is a risk of leakage.
In general, thermal pads are more of a necessary measure. They are used for two purposes:
-
If the gap between the contact plate of the heatsink and the surface of the cooled chip is too large to accommodate a layer of thermal paste (from 0.3 mm);
-
If the chip has been scalped and needs to be smoothed out.
Chip scalping is sometimes used to improve computer performance — when overclocking a processor or video card. But it is worth considering that then he becomes vulnerable to outside influences. Cooling the scalped chip is only necessary with thermal pads, which are highly likely not to leak over the years of use.
Which is better for a laptop — thermal paste or thermal pad
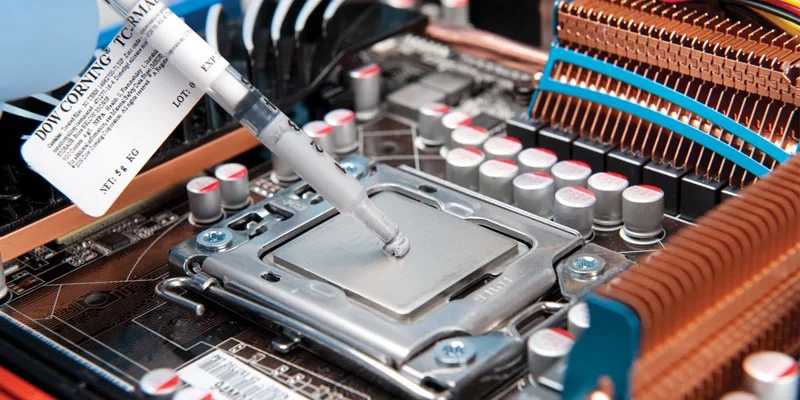
Of course, better quality thermal paste with high thermal conductivity. But if the gap between the chip and the contact plate of the heatsink is too large, then it is recommended to use a thermal pad.
Let’s compare these two thermal interfaces.
|
|
|
|
|
|
It is required to place a thin layer (0.1-0.3 mm) on a flat and smooth surface
|
It is enough to cut a rectangle and stick it on the chip. Placement on an uneven and rough surface is allowed (after scalping, for example)
|
|
|
73 W/mK
|
12 W/mK
|
|
|
May dry out, may leak
|
May leak
|
Thus, in terms of ease of use, the thermal pad wins. But for better implementation of cooling, it is recommended to use a cooler.
In general, there is a simple rule. If the manufacturer used a thermal pad, then it is better to install it. If thermal paste — then her.
How to organize cooling on a laptop
To avoid overheating, it is recommended to follow a few simple cooling tips:
-
Use thermal interfaces with high thermal conductivity. Recommended value — from 6 W / mK, on processors and video cards — from 10 W / mK;
-
Firmly press the contact soles of the heat pipes to the cooled chips. The stronger, the better;
-
Beware of dust on radiators. At least 1 time in half a year (or 2 times if there are animals in the house) remove the cooler and carefully blow through the grate with an air cleaner;
-
Try to keep laptops on flat hard surfaces. Avoid placing them on fabric or knees;
-
If the space around the keyboard is made of metal, avoid placing stickers or other “garbage” on it. This aluminum panel is also used for system cooling;
-
If the laptop continues to overheat — for example, due to prolonged use under excessive loads — then it is better to purchase a cooling pad with active coolers altogether.
Добавить комментарий
Для отправки комментария вам необходимо авторизоваться.