
Comparing Cat 5e and Cat 6 Standards
Network technologies are constantly evolving, trying to provide more and more bandwidth. And telecommunications equipment is also improving. It would be strange if today’s terabit data volumes were transmitted over some kind of two-wire ADSL, wouldn’t it? Therefore, it was replaced by Ethernet, and then fiber in general.
Nevertheless, it was Ethernet that became the generally accepted standard for laying local networks. It was made so by the cross-compatibility of equipment and the convenience of laying lines. However, with the increase in the amount of transmitted data, there was a need to increase the bandwidth of Ethernet.
This is how new categories of Ethernet interface began to appear. The most common in local networks at the moment (2019) are Cat 5e and Cat 6. These standards provide sufficient performance for working on a LAN and connecting computers, servers and other telecommunications equipment.
Nevertheless, there is a difference between these standards, and a very significant one. Let’s consider both.
Cat 5e standard
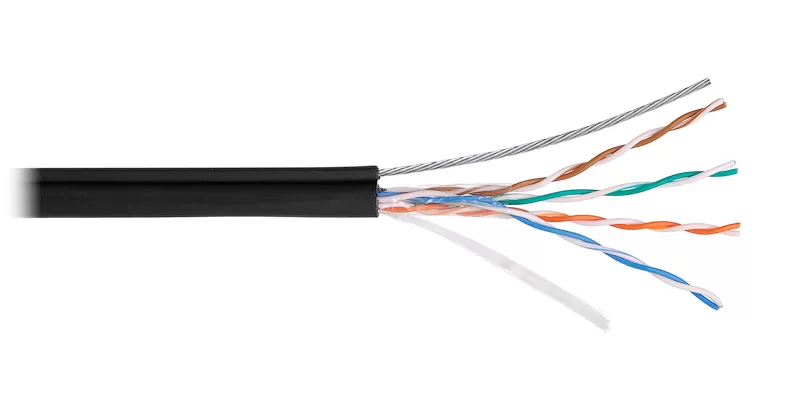
The Cat 5e Ethernet standard is designed for use in low-load networks, as it is focused on transmitting a signal with a frequency of 100 MHz. Its construction includes a nylon thread that enhances strength, tear resistance and bending resistance. However, the jacket (cambric) of the wire is relatively thin, which makes it quite vulnerable to interference.
But a thin shell greatly simplifies the gasket. Such a wire bends better and therefore can be used for installation in difficult conditions.
Cables of this standard are available in three versions — UTP, FTP and SFTP. The first are unshielded and therefore suitable for laying networks that do not require high protection of transmitted information from interference. For example, for home or office use. But STP cables are already complemented by a screen that protects against interference. They are designed for high-precision transmission of information in special conditions, as well as for laying near sources of electromagnetic fields (including electric motors in refrigerators and vacuum cleaners).
SFTP is intended for use near powerful sources of electromagnetic fields — generators, transformers, electrical substations. It shields both each twisted pair and all four pairs under the shell (cambric).
But the main thing is that the maximum information transfer rate over a category 5e interface is 1 gigabit per second. PoE is supported. The maximum laying length without amplification or connection to the «bridge» is 100 meters.
Cat 6 standard
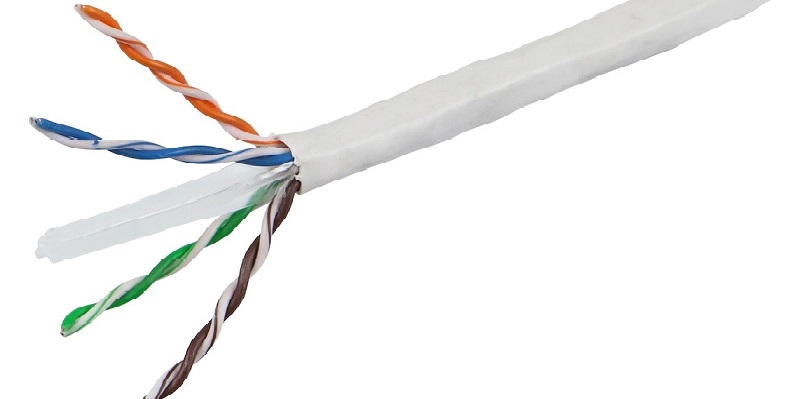
The Cat 6 standard is designed specifically for use in high-load networks. Its design includes highly woven twisted pairs with a large number of turns per linear centimeter. Thanks to this, the cable can withstand data transmission at a frequency of 250 MHz.
Increasing the frequency of the transmitted signal made it possible to increase the bandwidth of the interface. Networks based on it and related hardware support 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
Structurally, the wire of the sixth category differs from its predecessor in the increased thickness of the sheath. This helps to protect the transmitted information from external electromagnetic interference and interference from other cables, including power ones.
«Sixth category» is also available in shielded and unshielded versions. An SFTP version with two screens for laying near strong sources of electromagnetic fields is also available.
Cables of this type have one very important feature — the maximum transmitted frequency depends on the length of the wire. That is, the above 250 MHz wire is capable of transmitting only if the distance from the transmitter to the receiver does not exceed 55 meters. And with an increase in its cable, it can only cope with 100 MHz.
As a result, the highest bandwidth of 10 gigabits per second is only achieved at a length of up to 55 meters. With a greater distance between the receiver and the transmitter, it is only 1 gigabit per second. And the maximum length is 100 meters. PoE power transmission is also supported.
Difference between Cat 5e and Cat 6
Let’s summarize the information about these two standards in a comparative table:
|
|
|
|
|
Support 10 Mbps
|
There is
|
There is
|
|
Support 100 Mbps
|
There is
|
There is
|
|
Support 1Gb/s
|
There is
|
There is
|
|
Support 10 Gb/s
|
Not
|
Yes, but with distance restrictions
|
|
Power over Ethernet support
|
There is
|
There is
|
|
Limit transmitted frequency, MHz
|
100
|
250
|
|
Maximum length, m
|
100
|
100
|
|
Reinforcing structural elements for increased flexural and tensile strength
|
Nylon thread
|
thick shell
|
|
Shell thickness
|
Relatively small
|
Relatively large
|
|
Screen options (FTP, SFTP)
|
There is
|
There is
|
|
Comparative number of turns of a pair per linear unit
|
Small
|
big
|
|
Scope of use
|
Home, office
|
Highly loaded networks
|
At the same time, it is worth noting that the maximum throughput is indicated as a recommended, but not a limit. According to the studies, for short-term transmission over short distances (up to 30-40 meters), the 5e interface will cope with a 10-gigabit load, and the «sixth category» will withstand 500 MHz.
Добавить комментарий
Для отправки комментария вам необходимо авторизоваться.