Compare cauliflower and broccoli
Cauliflower and broccoli have some similarities in appearance and differ from all other varieties of cabbage (white, Peking, Brussels, kohlrabi, etc.). Some do not see any difference in them. However, they are two completely different vegetables with different chemical composition, taste, nutritional value and history. Our experts have learned all about broccoli and cauliflower and are ready to tell you how they differ.
Cauliflower: general information, composition, calories

Cauliflower is a member of the cruciferous family, an annual vegetable crop. Its edible part (head) is a huge inflorescence, consisting of many buds tightly pressed against each other with green leaves bordering them. It is these «flowers» that are eaten (and not the leaves, in contrast to the white one). Hence the name «color». The most familiar to us cabbage with a white-cream head, but there are varieties with orange, green and even purple buds.
Cauliflower has been known since ancient times. In his writings, the great physician Avicenna (1st century) recommends eating it to improve health in the winter.
Until the XII century, it was grown only in the countries of the Middle East. Then the Arabs brought this vegetable crop to Europe. For a long time it was called Syrian cabbage there.
Once Mark Twain wrote: «Cauliflower is ordinary (white) cabbage only with higher education.» And indeed it is. It is also good for health (has a similar composition of vitamins and minerals), but it is easier and faster to digest in the digestive tract, less likely to cause flatulence, and it contains more proteins.
Composition and calories
Cauliflower is 92% water and also contains:
-
2.5 g protein;
-
0.3 g fat (of which 0.243 g unsaturated omega-3 and omega-6);
-
6.3 g of carbohydrates (simple sugars — 3.8 g, fiber — 2.5 g, pectin — 0.6 g).
The calorie content of a raw vegetable is 30 kcal / 100 g. When cooked in the usual way or steamed, the energy value remains the same, and fried cauliflower, due to the addition of oil, will have a calorie content of 90-100 kcal.
The vegetable is rich not only in proteins, unsaturated fatty acids and fiber useful for the digestive tract, but also in a large amount of vitamins and minerals. In terms of vitamin C content, it exceeds white cabbage by 2 times (in 100 g — the daily norm is 90 mg).
The richest cauliflower:
-
folic acid (vitamin B9);
-
pantothenic acid (vitamin B5);
-
vitamin K;
-
boron;
-
silicon;
-
molybdenum;
-
potassium.
The composition of the «colored» varieties of vegetable crops includes natural dyes bioflavonoids — substances with antioxidant properties:
-
purple varieties contain anthocyanins;
-
in orange — carotenoids;
-
in green — chlorophyll.
The presence of betasitosterol, an antagonist of cholesterol and glucoraphanin, a precursor of the organic compound sulforaphane with powerful anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties, was established in the composition of the vegetable.
The benefits and harms of cauliflower

-
Cauliflower is recommended for dietary nutrition in diabetes mellitus, liver disease, cholelithiasis, atherosclerosis.
-
Due to the rich chemical composition, the use of a vegetable has a positive effect on the state of the body.
-
Improves the functioning of the digestive system.
-
Provides strong bones and healthy joints, prevents the risk of osteoporosis, arthrosis and arthritis.
-
Normalizes the work of the endocrine system, affects the production of hormones.
-
Strengthens the nervous system, improves sleep, prevents depression.
-
Promotes the full functioning of the heart, normalizes the water-salt balance in the body.
-
Prevents the deposition of sand in the bladder, protecting against urolithiasis.
-
Normalizes blood sugar levels, protects the walls of blood vessels from damage.
-
Reduces the level of cholesterol in the blood.
-
Protects against the development of inflammatory processes in the body and cancer.
-
Studies have shown that sulforaphane, contained in cauliflower, destroys cancer cells, slowing down the growth of malignant tumors of the breast, uterus, intestines, and prostate.
Despite the enormous value and benefits for the body, eating a vegetable can be harmful when:
-
gout;
-
hyperthyroidism;
-
renal failure;
-
hypertension;
-
after surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity.
Cauliflower can cause allergic reactions or indigestion in case of individual intolerance.
Broccoli: general information, composition and calorie content

Broccoli is an annual vegetable crop from the cruciferous family, a hybrid of garden cabbage obtained in the 16th century BC. e. ancient breeders of the Mediterranean. The word «broccoli» in Italian means «flowering stem, twig.»
Broccoli is the closest relative of cauliflower. On the stem, the height of which can be from 30 to 60 cm, many inflorescences are formed with small dark green buds. They are eaten before they bloom and turn yellow.
Until the 16th century, broccoli was not known outside of Italy, but with the beginning of the Great Geographical Discoveries, the vegetable crop became widespread throughout Europe. It was called «Italian asparagus» and was served as a side dish for meat, fish, and poultry.
In EU, broccoli began to be grown quite recently, but the number of its fans is constantly increasing. Many are attracted not by the taste of cabbage, but by its health benefits.
Composition and calories
Broccoli is 89% water, has a nutritional value of 34 kcal/100 g, of which:
-
6.64 g of carbohydrates (of which 3.3 g of dietary fiber);
-
2.82 g protein;
-
0.64 g fat.
Broccoli in terms of protein and dietary fiber (fiber and pectin) is the leader among all types of cabbage. In addition, it has a rich vitamin and mineral composition: 100 g cover the body’s daily need for ascorbic acid, vitamin K — by 85%. These vitamins are necessary for normal hematopoiesis and the functioning of connective and bone tissue.
Broccoli contains organic acids, phytosterols, and the eye-healthy carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin (23.5% of the recommended daily intake).
It also contains:
-
B vitamins;
-
vitamin E;
-
methylmethioninesulfonium;
-
boron;
-
silicon;
-
potassium;
-
sulfur;
-
iodine;
-
phosphorus.
Broccoli contains sulfurous chemical compounds glucosinolates, which are converted in the body into isothiocyanates (indole-3-carbinol and sulforaphane) — substances with powerful anti-cancer effects.
Broccoli extract is used for the manufacture of medicines and biological additives for the treatment and prevention of cancer.
The benefits and harms of broccoli

Broccoli is a source of substances with antioxidant, antitumor, choleretic and anti-inflammatory properties. The content of vitamin C, sulforaphane and indoles provides a powerful anti-cancer effect with regular consumption of the vegetable.
Studies have shown that the indoles in broccoli reduce the growth of estrogen-dependent malignancies. Women in whose body estrogens are rapidly destroyed are less susceptible to the occurrence and development of breast and uterine cancer.
Due to its beneficial properties, broccoli prevents the occurrence of cancer, developing from chronic inflammatory processes. It helps to cure cancer of the bladder, prostate, colon.
The pharmacological action of broccoli is not limited to anti-cancer activity. Due to its rich composition, the vegetable has a positive effect on the entire body:
-
normalizes the digestive system;
-
prevents the development of gastritis and gastric ulcer, enteritis and colitis;
-
normalizes blood sugar levels;
-
cleanses the body;
-
strengthens bones and teeth;
-
removes salt from the body;
-
strengthens the nervous system;
-
lowers cholesterol levels;
-
improves eyesight;
-
helps to get rid of excess weight;
-
improves the condition with mastopathy.
On the basis of broccoli extract, drugs are produced for the complex treatment of mastopathy: Indol Forte, Mastofit, Indinol.
Despite the beneficial properties of broccoli, its use can harm the body. Cabbage should be limited in the following diseases and conditions:
increased acidity of gastric juice and associated gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers (broccoli stimulates the secretion of hydrochloric acid and can further aggravate the situation);
thrombosis and a tendency to thicken the blood (due to the high content of vitamins K and C, which affect blood viscosity).
Sometimes broccoli causes allergic reactions in the form of skin rashes or severe indigestion due to individual intolerance.
Comparative table of vegetables on the composition of vitamins and minerals
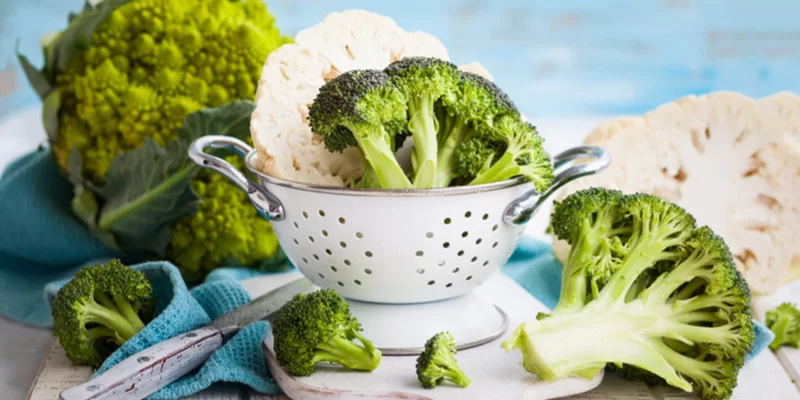

|
|
|
|
|
Vitamins:
|
|
|
|
IN 1
|
0.13 mg (7%)
|
0.07 mg (5%)
|
|
IN 2
|
0.12 mg (6%)
|
0.12 mg (6%)
|
|
AT 5
|
0.9 mg (18%)
|
0.57 mg (11%)
|
|
AT 6
|
0.16 mg (8%)
|
0.18 mg (9%)
|
|
AT 9
|
220 mcg (41%)
|
63 mcg (16%)
|
|
FROM
|
90 mg (100%)
|
100 mg (110%)
|
|
E
|
—
|
0.78 mg (5%)
|
|
To
|
16 mg (13%)
|
101 mg (90%)
|
|
beta carotene
|
102 mcg (1.2%)
|
361 mcg (7%)
|
|
Methylmethioninesulfonium (vitamin U)
|
6 mg (2.5%)
|
9 mg (7%)
|
|
Lutein + Zeaxanthin
|
—
|
1405 mcg (23.5%)
|
|
Minerals:
|
|
|
|
Potassium
|
250 mg (8%)
|
316 mg(13%)
|
|
Phosphorus
|
50 mg (6%)
|
66 mg (8%)
|
|
Bor
|
500 mcg (714%)
|
185 mcg (264%)
|
|
Iron
|
1.3 mg (8%)
|
0.73 mg (4%)
|
|
Sulfur
|
85 mg (8.5%)
|
140 mg(14%)
|
|
Silicon
|
22 mg (73%)
|
78 mg(260%)
|
|
Iodine
|
13 mcg (7.2%)
|
15 mcg(10%)
|
|
Molybdenum
|
8 mcg (12%)
|
—
|
Similarities and differences

Broccoli and cauliflower belong to the same cruciferous family and are «close relatives». No wonder they are similar. But there are significant differences between these two vegetable crops.
Similarities
They have a similar content of nutrients and dietary properties.
These vegetables contain significantly more vitamin C and proteins than other members of the cabbage family.
Rich in B vitamins, beta-carotene, methylmethiosulfonium, which protects the digestive system from the development of inflammatory diseases.
They contain special substances glucosinolates, which prevent the formation and growth of cancer cells in the tissues of the body.
Of the minerals, they contain a large amount of boron, silicon, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, and iron.
Both vegetables contain fiber, but it is much less than in white cabbage. Therefore, they do not irritate the gastric mucosa, are easily digested. In boiled form, they are allowed and recommended for nutrition in pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis (with reduced function), gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer.
Both types of cabbage have high taste qualities.
Inflorescences (heads) are used for food, not leaves.
They have a low calorie content and a low glycemic index (15 units), therefore they are considered ideal products for weight loss by nutritionists.
Broccoli and cauliflower contain components that help fight excess weight:
-
tartronic acid — interferes with the metabolism in the body, prevents the conversion of excess carbohydrates into body fat;
-
glucoraphanin — stabilizes blood sugar levels, increases glucose tolerance, helping to control appetite;
-
dietary fiber and enzymes improve the functioning of the pancreas and the digestive system as a whole;
-
sulforaphane — destroys bacteria in the intestines, the toxins of which contribute to the appearance of excess weight.
The rich biochemical composition, dietary properties and taste make broccoli and cauliflower unique food products. They can be eaten for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes — these vegetable crops protect against the development of many diseases: cancer, atherosclerosis, gastric ulcer, obesity, diabetes.
Differences
Despite the fact that these varieties of cabbage belong to the same family, they differ from each other in several ways:
-
in appearance: green broccoli, and cauliflower, mostly white-cream in color (only some varieties are really “colored”), its inflorescences are smaller and not so dense;
-
in terms of vitamin and mineral composition: broccoli is somewhat richer, although cauliflower wins in terms of the content of folic acid and boron;
-
to taste: in cauliflower it is softer, in broccoli it is a little spicy, grassy;
-
in terms of protein content: broccoli contains more of it;
-
according to the history of occurrence: color appeared earlier and was distributed over most of the globe;
-
according to growing conditions: cauliflower requires good lighting, air temperature 15-180C and fertile soil, and broccoli grows faster in damp, cool weather at a temperature of 18-23 0C, it needs frequent watering;
-
in terms of ripening: to grow a crop, it takes less time for broccoli — 1-1.5 months from the date of planting seedlings is enough for the appearance of mature heads, for cauliflower — at least 3 months.
-
on anti-cancer properties: broccoli is considered the most effective and useful vegetable that prevents the development of cancer.
Thus, broccoli and cauliflower are different vegetable crops that have their own characteristics and differ from each other in many ways.
Expert opinion
Broccoli and cauliflower are two of the tastiest and healthiest members of the cruciferous family. Due to the richness of their biochemical composition, both types of vegetable crops, when used regularly, protect the body from the development of many diseases, including malignant tumors. But the anti-cancer properties of broccoli are much stronger — based on the extract of this vegetable, various drugs and biological food supplements are produced.
As for the taste, here, rather, for an amateur: someone likes broccoli more, and someone prefers cauliflower.
We recommend including both vegetables in your diet — together they will bring double the benefits to the body.

Добавить комментарий
Для отправки комментария вам необходимо авторизоваться.